Calcite
Natural inorganic pigmentComposition and Properties of Calcite
Calcite is the mineral form of calcium carbonate CaCO3. There are other forms of calcium carbonate such as marble and also aragonite and vaterite, all of which have been used in painting. Calcite can be found in nature mainly in the form of chalk which had been formed from the fossil remains of marine algae.
The pigment is very stable under normal conditions but it dissolves in all acids under the evolution of carbon dioxide gas. It is lightfast and it does not darken in contact with environmental pollutants such as hydrogen sulfide and is also compatible with all other pigments.

Pigment

Painted swatch
Names
Alternative names
Chalk, lime white, St John’s white
Color Index
PW 18, CI 77220
Word origin
Chalk: from Old English cealc “chalk, soft white limestone; lime, plaster; pebble,” a West Germanic borrowing from Latin calx “limestone, lime (crushed limestone), small stone,” from Greek khalix “small pebble”
From Online Etymology Dictionary
Calcite: from German Calcit, coined by Austrian mineralogist Wilhelm Karl von Hardinger (1795-1871) from Latin calx (genitive calcis) “lime”.
From Online Etymology Dictionary
Kreide, Kalzit
German
Craie
French
Creta
Italian
Creta
Spanish
Preparation
Chalk is being quarried in England, Belgium, Germany, and other European countries. The raw material is sometimes left to weather and is then ground under water and dried.
History of Use
Chalk and the other forms of calcium carbonate have been in use since antiquity mainly as a component for grounds.
References
(1) Rohleder J. The history of chalk. In: Tegethoff F.W. (eds) Calcium Carbonate. Birkhäuser, Basel 2001
Examples of use
Dirk Bouts, The Entombment, probably 1450
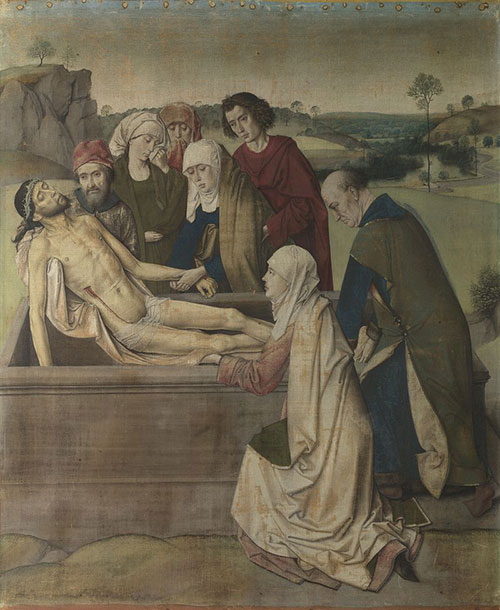
The upper part of the head covering of Mary is painted in chalk highlighted with small amounts of lead white.
Identification
Fiber optics reflectance spectra (FORS)
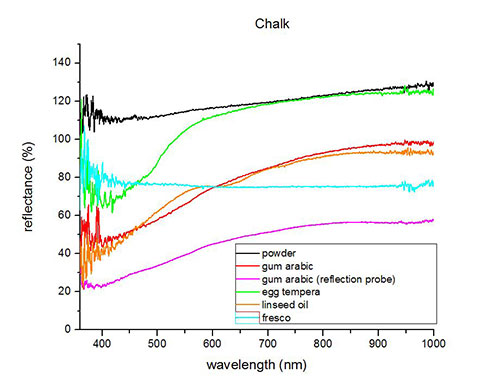
Spectra by A. Cosentino, Cultural Heritage Science Open Source (CHSOS)
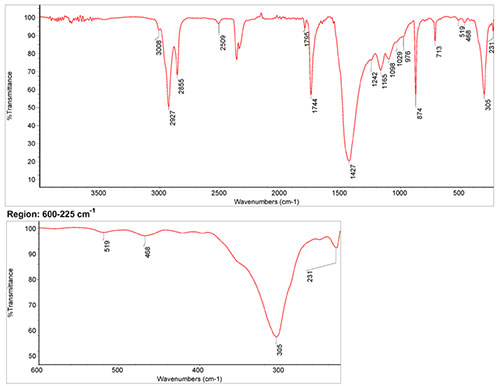
IR Spectrum
Spectrum by S. Vahur, Database of ATR-IR spectra of materials related to paints and coatings, University of Tartu, Estonia
Raman Spectrum
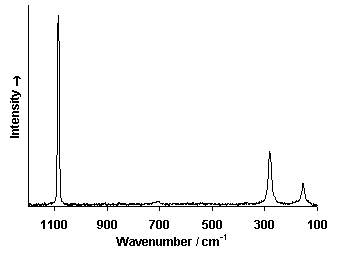 Spectrum by Ian M. Bell, Robin J.H. Clark and Peter J. Gibbs, Raman Spectroscopic Library
Spectrum by Ian M. Bell, Robin J.H. Clark and Peter J. Gibbs, Raman Spectroscopic Library
University College of London
X-Ray Fluorescence Spektrum (XRF)
XRF Spectrum in the Free XRF Spectroscopy Database of Pigments Checker, CHSOS website.
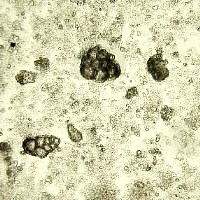
Microphotograph
image © Volker Emrath
Further Reading
References
(1) Gettens, R. J., West Fitzhugh, E. and Feller, R. L., Calcium Carbonate Whites in Artists’ Pigments. A Handbook of Their History and Characteristics, Vol. 2: A. Roy (Ed.) Oxford University Press 1993, p. 203-26. Available as pdf from the National Gallery of Art.
(2) S. Muntwyler, J. Lipscher, HP. Schneider, Das Farbenbuch, 2nd. Ed., 2023, alataverlag Elsau, pp. 60-61.