Gamboge
Natural organic pigmentComposition and Properties of Gamboge
Gamboge is a natural resin produced by trees in southeast Asia. Its main coloring components are the two substances shown below.
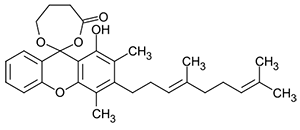
β-Guttilacton
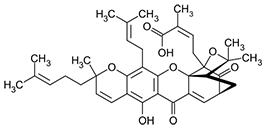
Gambogic acid
The pigment is transparent and can be used in oil painting as a glaze. It changes its color to orange in contact with alkalis and is not very lightfast. It is not compatible with alkaline pigments and possibly with lead white.

Pigment

Painted swatch
Video: 'Old and New Gamboge by Winsor & Newton' by The Spin Doctor
Names of Gamboge
Alternative names
Gambogium, gummi gutti, gamma gitta, gom gutae
Color Index
Natural Yellow NY 24
Word origin
From Modern Latin cambogium, ultimately from the source of the place name Cambodia.
From Online Etymology Dictionary
Gummigutti
German
Gomme-gutte
French
Gomma gutta
Italian
Gomaguta or gutagamba
Spanish
Preparation
The bark of the trees is incised and the raw material is then collected in bamboo tubes.

Raw material
History of Use
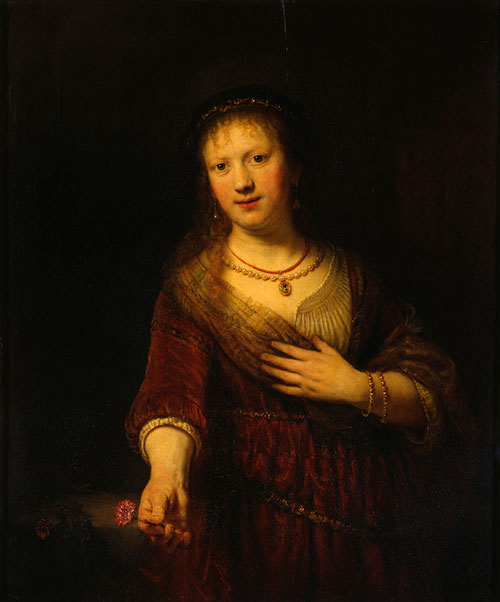
Gamboge was in use since around the 8th century in Japan and China. Its use in European oil painting is not very well documented and the reported occurrences are not always substantiated by experimental procedures. H. Kühn reported the use of the pigment in the Rembrandt painting below. A mixture of this pigment and Prussian blue was employed under the name Hooker’s green in watercolour painting.
References
(1) Kühn, H., Die Pigmente in den Gemälden der Schack-Galerie, in: Bayerische Staatsgemäldesammlungen (Ed.) Schack-Galerie (Gemäldekataloge Bd. II), München 1969, p. 229-230
Examples of use
Rembrandt van Rijn, Saskia van Uylenburgh as Flora, 1641
Identification
Fiber Optics Reflectance Spectra (FORS)
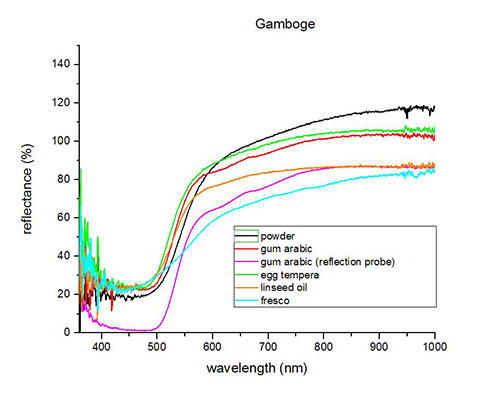 Spectra by A. Cosentino, Cultural Heritage Science Open Source (CHSOS)
Spectra by A. Cosentino, Cultural Heritage Science Open Source (CHSOS)
Raman Spectrum
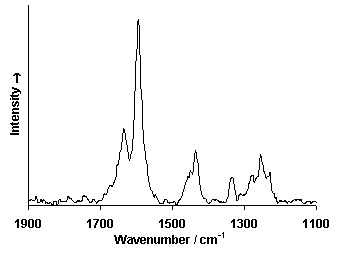
Spectrum by Ian M. Bell, Robin J.H. Clark and Peter J. Gibbs, Raman Spectroscopic Library
University College of London.
X-Ray Fluorescence Spektrum (XRF)
XRF Spectrum in the Free XRF Spectroscopy Database of Pigments Checker, CHSOS website.
NMR Spectroscopy
NMR spectra of most of the constituents of gamboge have been published by Ollis et al. (1)
(1) Ollis, W.D., Ramsay, M.V.J., Sutherland, I.O. and Mongkolsuk, S., The Constitution of Gambogic Acid, Tetrahedron 21, 1965, 1453-1470
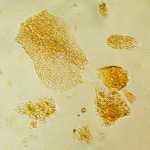
Microphotograph
image © Volker Emrath
Further Reading
References
(1) Winter, J., Gamboge, in Artists’ Pigments. A Handbook of Their History and Characteristics, Vol. 3: FitzHugh, E.W. (Ed.) Oxford University Press 1997, p. 143 – 155. Available as pdf from the National Gallery of Art.
(2) S. Muntwyler, J. Lipscher, HP. Schneider, Das Farbenbuch, 2nd. Ed., 2023, alataverlag Elsau, pp. 154-155.