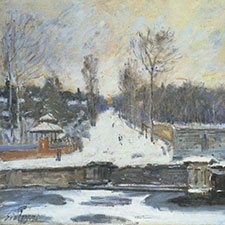Cobalt Blue
Artificial inorganic pigmentComposition and Properties of Cobalt Blue
Cobalt blue (Thénard’s blue) is a mixed oxide of cobalt and aluminum CoO • Al2O3. It can also be considered to be cobalt (II)-aluminate with the formula of CoAl2O4.
It is very stable and is unaffected by heating and by concentrated acids and alkalis. The pigment is practically unaffected by light and is compatible with all other pigments.
Art Teachers' Materials
Richly illustrated presentation on the properties, preparation, identification and use of this pigment
Names of Cobalt Blue
Alternative names
Thénard’s blue
Color Index
PB 28, CI 77346
Word origin
From the German word Kobold meaning evil house spirit. The name was originated by medieval miners who believed, that cobalt ores made it difficult to extract silver from silver ore.
Kobaltblau
German
bleu de cobalt
French
Azzurro di cobalto
Italian
Azul de cobalto
Spanish
Preparation of Cobalt Blue
Attention: Cobalt compounds are highly toxic and should not be handled by people not trained to do so.
Cobalt blue can be prepared by heating a mixture of cobalt (II)-chloride CoCl2 · 6H2O and aluminum oxide Al2O3.


The mixture is then heated in a test tube with the aid of a Bunsen burner for several minutes.

The resulting mass of cobalt blue is finely pulverized in a mortar.
Video: 'Cobalt Blue Part 1' by The Alchemical Arts
References
(1) Citoyen Thénard, Considérations générales sur les couleurs, suivies d’un procédé pour préparer une couleur bleue aussi belle que l’outremer, Journal des Mines 86: 128–136 (pdf of the original article by Thénard)
(2) Gehlen, A.F. (1803). “Ueber die Bereitung einer blauen Farbe aus Kobalt, die eben so schön ist wie Ultramarin. Vom Bürger Thenard“. Neues allgemeines Journal der Chemie, Band 2 (H. Frölich.). German translation from Thénard, L.J. (1803, (Brumaire, XII)) (pdf of the translation of the original article by Thénard into German).
History of Use
Cobalt blue has been used since its first preparation by Thénard in 1803-04 and it is still one of the most popular blue pigments. The following graph gives the frequency of its use in the paintings of the Schack Collection in the Bavarian State Art Collections in Munich (1).

An extensive collection of occurrences of this pigment in paintings from several historical periods can be found in the blog post ‘Pigment: Cobalt Blue, the 19th-century sky‘ by The Eclectic Light Company.
References
(1) Kühn, H., Die Pigmente in den Gemälden der Schack-Galerie, in: Bayerische Staatsgemäldesammlungen (Ed.) Schack-Galerie (Gemäldekataloge Bd. II), München 1969.
Examples of use
William Turner, The Fighting Téméraire tugged to her last berth to be broken, 1838
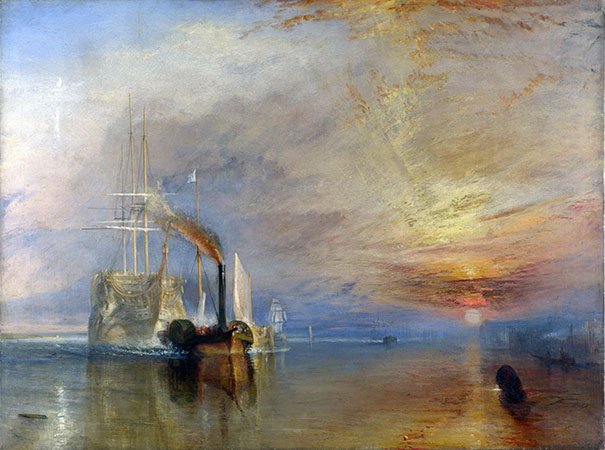
Pierre-Auguste Renoir, The Umbrellas, 1880-86

The clothes of the mother and her daughters on the right are painted in cobalt blue, while the grey-blue dress of the woman in the left part of the image contains artificial ultramarine.
Vincent van Gogh, The Starry Night, 1889
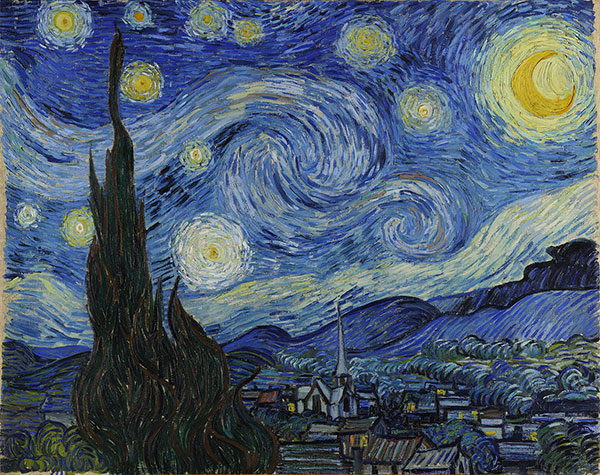

The brighter blue parts of the sky are painted in cobalt blue, while the darker more intense parts contain artificial ultramarine.
Identification
Fiber Optics Reflectance Spectrum (FORS)
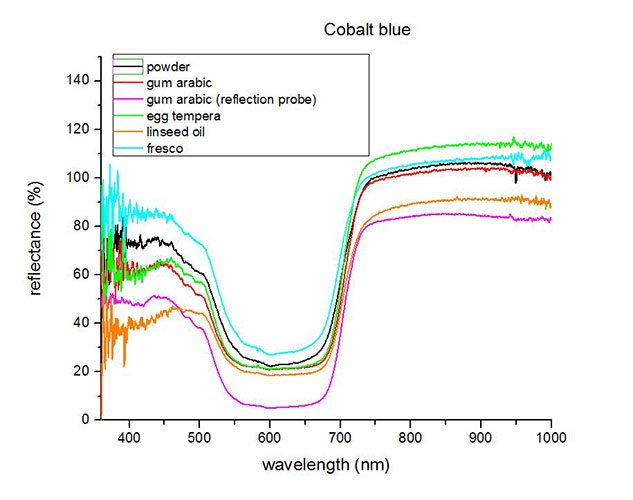
Spectra by A. Cosentino, Cultural Heritage Science Open Source (CHSOS)
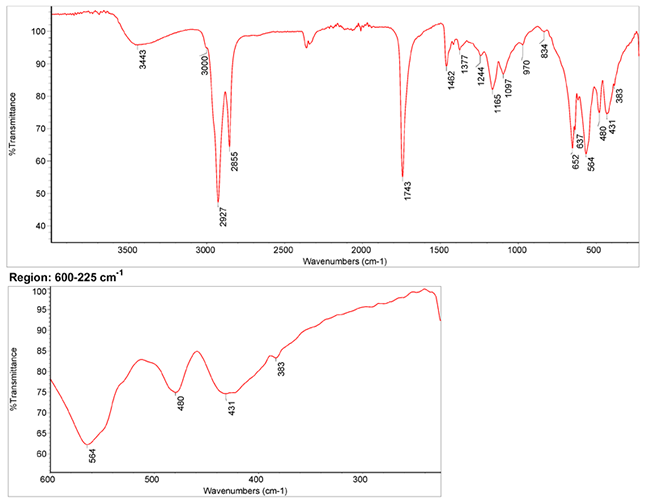
Infrared Spectrum
- Spectrum by S. Vahur, Database of ATR-IR spectra of materials related to paints and coatings, University of Tartu, Estonia
2. IR-Spectrum in the ATR-FT-IR spectra of different pure inorganic pigments, University of Tartu, Estonia
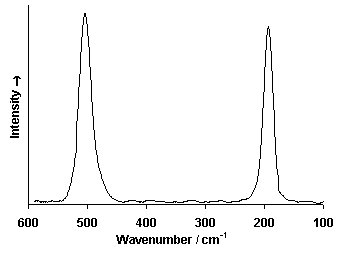
Raman Spectrum
Spectrum by Ian M. Bell, Robin J.H. Clark and Peter J. Gibbs, Raman Spectroscopic Library University College of London
X-Ray Fluorescence Spektrum (XRF)
XRF Spectrum in the Free XRF Spectroscopy Database of Pigments Checker, CHSOS website.
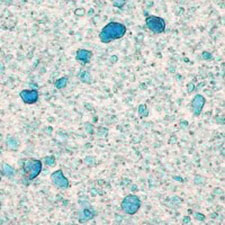
Microphotograph
image © Volker Emrath
Further Reading
References
(1) Roy, A. Cobalt blue, in Artists’ Pigments, A Handbook of Their History and Characteristics, Vol. 4, Berrie, B.H., Ed., National Gallery of Art Washington, 2007.
(2) Citoyen Thénard, Considérations générales sur les couleurs, suivies d’un procédé pour préparer une couleur bleue aussi belle que l’outremer, Journal des Mines 86: 128–136 (pdf of the original article by Thénard)
(3) Gehlen, A.F. (1803). “Ueber die Bereitung einer blauen Farbe aus Kobalt, die eben so schön ist wie Ultramarin. Vom Bürger Thenard“. Neues allgemeines Journal der Chemie, Band 2 (H. Frölich.). German translation from Thénard, L.J. (1803, (Brumaire, XII)) (pdf of the translation of the original article by Thénard into German).
(4) S. Muntwyler, J. Lipscher, HP. Schneider, Das Farbenbuch, 2nd. Ed., 2023, alataverlag Elsau, pp. 92-93.