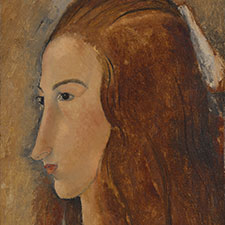Zinc White
Artificial inorganic pigmentComposition and Properties of Zinc White
Zinc white is zinc oxide with the formula ZnO.

Pigment

Painted swatch
Video 'Titanium & Zinc White' by CITY STATIONERY GROUP SAL
Names
Alternative names
Snow white, Chinese white
Color Index
PW 4, CI 77947
Word origin
Zinc: from German Zink, perhaps related to Zinke “prong, point;” said to have been used first by Paracelsus (c. 1526) on analogy of the form of its crystals after smelting. Zinke is from Old High German zint “a point, jag,” from Proto-Germanic *teng– “tine”
From Online Etymology Dictionary
Zinkweiss
German
Blanc de zinc
French
Bianco di zinco
Italian
Blanco de cinc
Spanish
Preparation
Zinc oxide can be prepared in three different ways
1. Indirect (French) process: metallic zinc is vaporized at approximately 1000 °C at which temperature it spontaneously ignites and forms zinc oxide.
2. Direct (American) process: the starting material for this process are either zinc ores or industrial byproducts. In the first step, the zinc-containing material is reduced by a carbon-containing agent such as anthracite at high temperatures. The zinc vapour is then ignited and forms zinc oxide.
3. Wet process: Soluble zinc salts are treated with a solution of sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide. The resulting precipitation of zinc carbonate or hydroxide is then calcinated at about 800 °C to form zinc oxide.
References
(1) Kuhn, H., Zinc White, in Artists’ Pigments. A Handbook of Their History and Characteristics, Vol. 1, L. Feller, Ed., Cambridge University Press, London 1986, p. 169 – 186. Available as pdf from the National Gallery of Art.
(2) Amir Moezzi, Andrew M. McDonagh, Michael B. Cortie, Zinc oxide particles: Synthesis, properties and applications, Chemical Engineering Journal, Volumes 185–186, 15 March 2012, Pages 1–22.
History of Use
Zinc white has been known as a mineral since antiquity but was not used as a pigment until the 18th century. The following graph gives the frequency of its use in the paintings of the Schack Collection in the Bavarian State Art Collections in Munich (1).

References
(1) Kühn, H., Die Pigmente in den Gemälden der Schack-Galerie, in: Bayerische Staatsgemäldesammlungen (Ed.) Schack-Galerie (Gemäldekataloge Bd. II), München 1969.
Examples of use
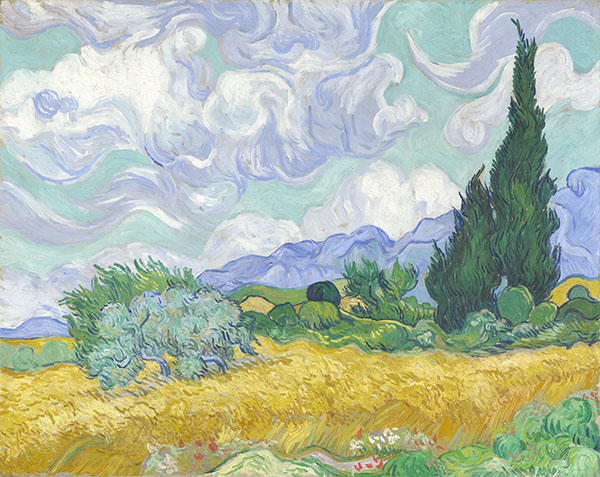
Vincent van Gogh, Wheat Field with Cypresses, 1889
The white sky (Nr 1) is painted in pure zinc white, the blue sky (Nr 2) contains zinc white and cobalt blue.

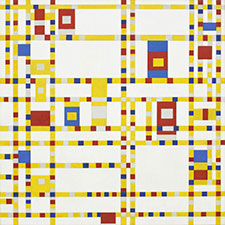
Amadeo Modigliani, Jeanne Hébuterne, 1919
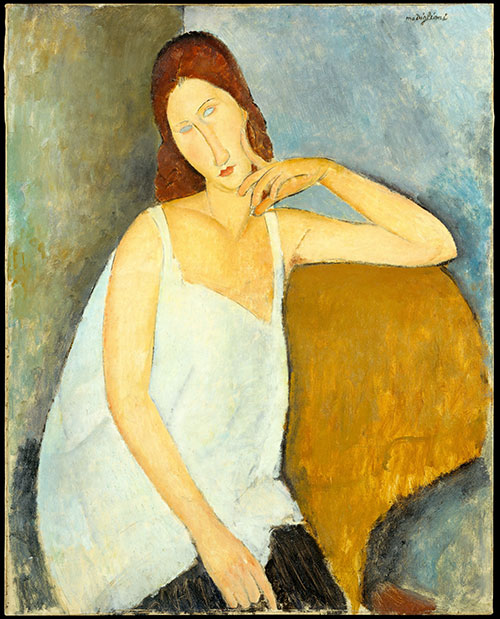

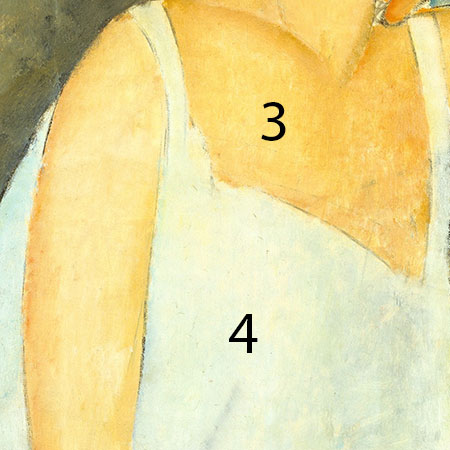
3 Skin: lead white, zinc white, chrome yellow, and/or chrome orange with small amounts of yellow ochre
4 White chemise: lead white, and zinc white

Identification
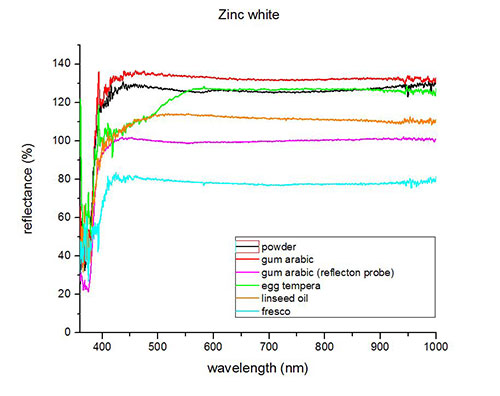
Fiber optics reflectance spectra (FORS)
Spectra by A. Cosentino, Cultural Heritage Science Open Source (CHSOS)
IR Spectrum
IR-Spectrum in the ATR-FT-IR spectra of different pure inorganic pigments, University of Tartu, Estonia
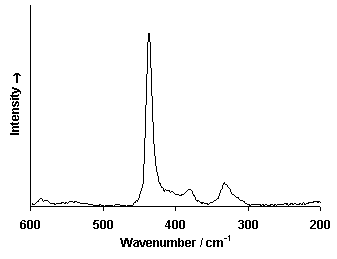
Raman Spectrum
Spectrum by Ian M. Bell, Robin J.H. Clark and Peter J. Gibbs, Raman Spectroscopic Library
University College of London
X-Ray Fluorescence Spektrum (XRF)
XRF Spectrum in the Free XRF Spectroscopy Database of Pigments Checker, CHSOS website.
References
(1) Mauro Bacci, Marcello Picollo, Giorgio Trumpy, Masahiko Tsukada and Diane Kunzelman, Non-Invasive Identification of White Pigments on 20th-Century Oil Paintings by Using Fiber Optic Reflectance Spectroscopy, Journal of the American Institute for Conservation, Vol. 46, No. 1 (Spring, 2007), pp. 27-37.
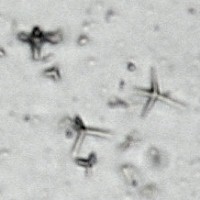
Microphotograph
image © Volker Emrath
Further Reading
References
(1) Kuhn, H., Zinc White, in Artists’ Pigments. A Handbook of Their History and Characteristics, Vol. 1, L. Feller, Ed., Cambridge University Press, London 1986, p. 169 – 186. Available as pdf from the National Gallery of Art.
(2) General properties of ZnO, in Hadis Morkoç, Ümit Özgür, Zinc Oxide: Fundamentals, Materials and Device Technology, Wiley Online Library 2009 (pdf).
(3) S. Muntwyler, J. Lipscher, HP. Schneider, Das Farbenbuch, 2nd. Ed., 2023, alataverlag Elsau, p. 119.